Devops | Backend Dev
HTTP security headers (in CloudFront and Netlify)
March 11, 2023
Adding security headers to a website is one of the fundamental forms of preparation in cyber security. There are plenty of articles describing each specific HTTP header and what they protect against, so I won’t outline them here, but here is how they’re set up with CloudFront and Netlify.
securityheaders.com is very useful for checking which headers exist on a website.
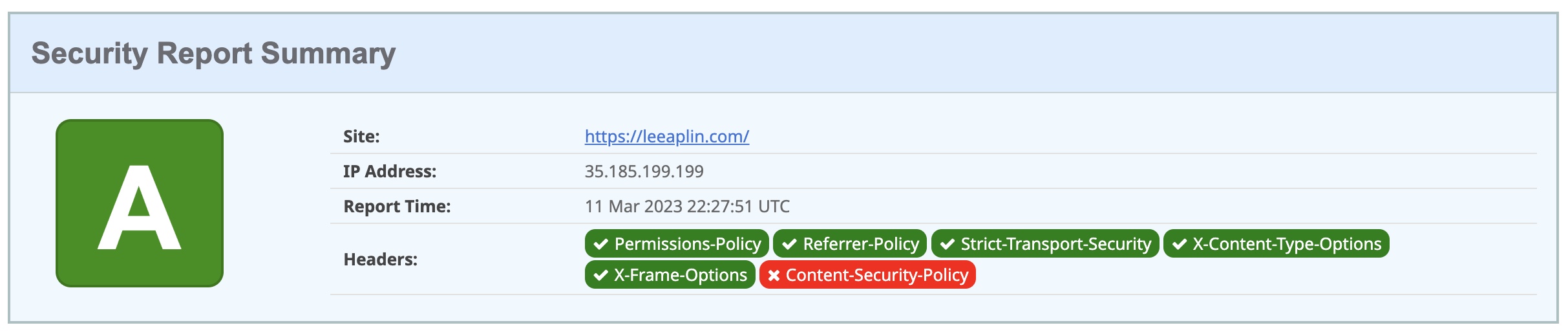
Adding HTTP headers in CloudFront
CloudFront makes it really easy to set security and custom HTTP response headers by using a response header policy. It is even simpler because all of the basic security headers can be added using an AWS managed policy.
- In AWS go to the CloudFront dashboard
- Click on Policies and go to the Response Header Policies tab
- Create a new policy and click on managed policies to select SecurityHeadersPolicy
- In a CloudFront distribution associate this newly create policy with your behaviours as appropriate
The managed SecurityHeadersPolicy adds the following headers:
- Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin
- Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000
- X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
- X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
- X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
Adding a custom policy is equally as simple because all of the security headers mentioned above can be enabled using checkboxes when created the policy. There is also the option for adding custom headers.
Adding security headers in Netlify
This website is hosted using Netlify, which allows custom configuration by adding a netlify.toml file into the root of your project.
There are lots of available customisations which you can read about in the Netlify documentation. Adding HTTP headers can be done by adding them into the netlify.toml file. For example:
[[headers]]
for = "/*"
[headers.values]
X-Content-Type-Options = " nosniff"
Cache-control = "no-store,max-age=0"
Referrer-Policy = "no-referrer"
X-Frame-Options = "DENY"
X-XSS-Protection = "1; mode=block"
Permissions-Policy = "geolocation=(self), midi=(), sync-xhr=(), camera=(), microphone=(), magnetometer=(), gyroscope=(), fullscreen=(), payment=()"In the above, all of the listed security headers are served when a client makes a request, to all pages of the site.
Multiple URL paths can be set with different headers assigned by creating additional headers tables for each path.
Once this file is set up, Netlify will read any custom configurations and replace the default settings with any specified here.
Check the documentaion for more information about adding custom headers in Netlify.
Summary
Security headers are a very important defence against lots of common vulnerabilities, but enabling them on your site can be done quite simply. If you are using CloudFront, or your site is hosted on Netlify (like this one) the configurations outlined here should get you set up with the essential headers quickly and easily.